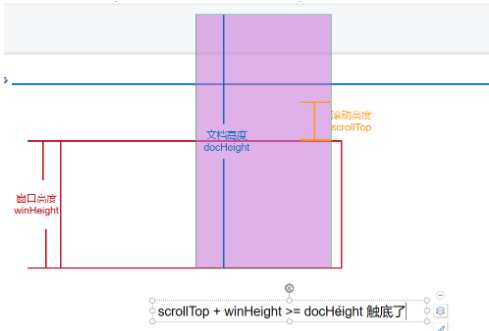
三个高度的获取
let st =
window.pageYOffset ||
document.documentElement.scrollTop ||
document.body.scrollTop;
// 浏览器窗口(文档)的可视高度(windowHeight):(就是你肉眼可见的那部分全屏高度)
let windowHeight =
window.innerHeight ||
document.documentElement.clientHeight ||
document.body.clientHeight;
// 文档的真实高度(scrollHeight):
let scrollHeight =
document.documentElement.scrollHeight || document.body.scrollHeight;
/* 这里提示:当 windowHeight + st >= scrollHeight 时就表示滚到底了。 */
用vue来实现一个pc端滚动加载更多,没有使用UI框架,纯手工
实现思路:
1.判断浏览器滚动条是否到达底部,如果到达底部,则使用axios拉取数据
2.拉取成功后,更新数据
布局方式
这里采用了头尾固定和中间高度自适应的布局方式,中间内容块高度没有设置,所以滚动条是在div的内容区域的,并不是在页面上,然而中间内容区域出现一个滚动条不是很好看,所以可以调整一下滚动条样式
/*html代码*/
<div id="dHead"></div>
<div id="dBody">
<div class="mycontent">
</div>
</div>
<div id="dFoot"></div>
/*css代码*/
#dHead {
height:100px;
width:100%;
position:absolute;
z-index:5;
top:0;
}
#dBody {
width:100%;
overflow:auto;
top:100px; //top
position:absolute;
z-index:10;
bottom:100px; //bottom
}
#dFoot {
height:100px;
width:100%;
position:absolute;
z-index:200;
bottom:0;
}
/*滚动条样式*/
/*定义滚动条高度及背景 宽高分别对应横竖滚动条的尺寸*/
::webkit-scrollbar{
width:1px; /*宽高可调节,如果为0,则消失*/
height:1px;
background-color:#eaeaea;
}
/*定义滚动条轨道,内阴影+圆角*/
::webkit-scrollbar-track{
-webkit-box-shaow:inset 0 0 6px rgba(0,0,0,0.3)
border-radius:10px;
background-color:#f5f5f5;
}
/*定义滑块 内阴影+圆角*/
::webkit-scrollbar-thumb{
border-radius:10px;
-webkit-box-shadow:inset 0 0 6px rgba(0,0,0,.3)
background-color:#555;
}
滚动条判断
是对元素的滚动监听,项目中是中间内容的最外层元素,这里碰到一个坑就是对中间滚动元素监听都无效,必须对中部内容块的最外层元素监听。需要获取到元素的dom节点,在vue组件里面使用的是原生js的监听事件。
/*html*/
<div id="dBody" ref='viewbox'>
<div class="mycontent">
</div>
/*vue*/
methods:{
setpage(){
if (this.nomore &&!this.loaded) return;//到达底部不再执行
if(this.$refs.viewBox.scrollTop+ this.$refs.viewBox.offsetHeight+20 >=
this.$refs.viewBox.scrollHeight){
this.loadingTip=true //loading提示语
axios.get('/api/v1/topics?tab='+this.tabName+'&page='(++this.page)+'&limit=10')
.then(
res=>{
let arr=res.data.data;
if(arr.length===0){
//some tips
this.loaded=false
this.nomore=true//没有更多
return
}
// ES5的合并数组
// arr1.concat(arr2, arr3);
// ES6的合并数组
//[...arr1, ...arr2, ...arr3]
this.site=[...this.site,...arr]
this.loadingTip=false
}
)
.catch(err=>{
console.log(err)
})
}
}
}
函数节流
发现一个问题就是当浏览器到达底部时,会多次触发函数,为了解决这个问题,进行函数节流。
浏览器中某些计算和处理要比其他的昂贵很多。例如,DOM 操作比起非 DOM 交互需要更多的内存和 CPU 时间。连续尝试进行过多的 DOM相关操作可能会导致浏览器挂起,有时候甚至会崩溃。尤其在 IE 中使用 onresize 事件处理程序的时候容易发生,当调整浏览器大小的时候,该事件会连续触发。
在 onresize 事件处理程序内部如果尝试进行 DOM 操作,其高频率的更改可能会让浏览器崩溃。为了绕开这个问题,你可以使用定时器对该函数进行节流。
函数节流背后的基本思想是指,某些代码不可以在没有间断的情况连续重复执行。第一次调用函数,创建一个定时器,在指定的时间间隔之后运行代码。当第二次调用该函数时,它会清除前一次的定时器并设置另一个。如果前一个定时器已经执行过了,这个操作就没有任何意义。然而,如果前一个定时器
尚未执行,其实就是将其替换为一个新的定时器
在这个项目中,是这样的
mounted(){
this.$refs.viewBox.addEventListener('scroll',
this.throttle(this.setpage,200),false)
},
methods:{
throttle(fn,delay,atleast){
/**函数节流方法
@param Function fn 延时调用函数
@param Number dalay 延迟多长时间
@param Number atleast 至少多长时间触发一次
@return Function 延迟执行的方法
*/
let timer = null;
let previous = null;
return function () {
var now = +new Date();
if ( !previous ) previous = now;
if ( atleast && now - previous > atleast ) {
fn();
// 重置上一次开始时间为本次结束时间
previous = now;
clearTimeout(timer);
} else {
clearTimeout(timer);
timer = setTimeout(function() {
fn();
previous = null;
}, delay);
}
}
},
}
拉取数据,加载loading
在拉取数据时,可能会有时间缓存,在等待时间里使用了一个loading图,转圈的圆环,css3写的简单转圈效果,一个画了270°的圆。使用了axios拉取数据,在回调函数中隐藏loading缓冲,因为已经拉取完成了。
.loadingTip{
height:50px;
line-height:50px;
text-align:center;
color:#666666;
}
.loadingTip::before{
content:'';
width: 20px;
height:20px;
border-radius:100% 100% 100% 0;
border: 1px solid red;
display: inline-block;
border-bottom: none;
border-left:none;
box-sizing: border-box;
vertical-align:sub;
-webkit-animation:loading 1s linear infinite;
}
@keyframes loading{
0%{
transform:rotate(0deg)
}
100%{
transform:rotate(360deg)
}
}
总结记录
唉,真的想哭,或许以后可以优化成更优雅的写法








Comments | NOTHING